
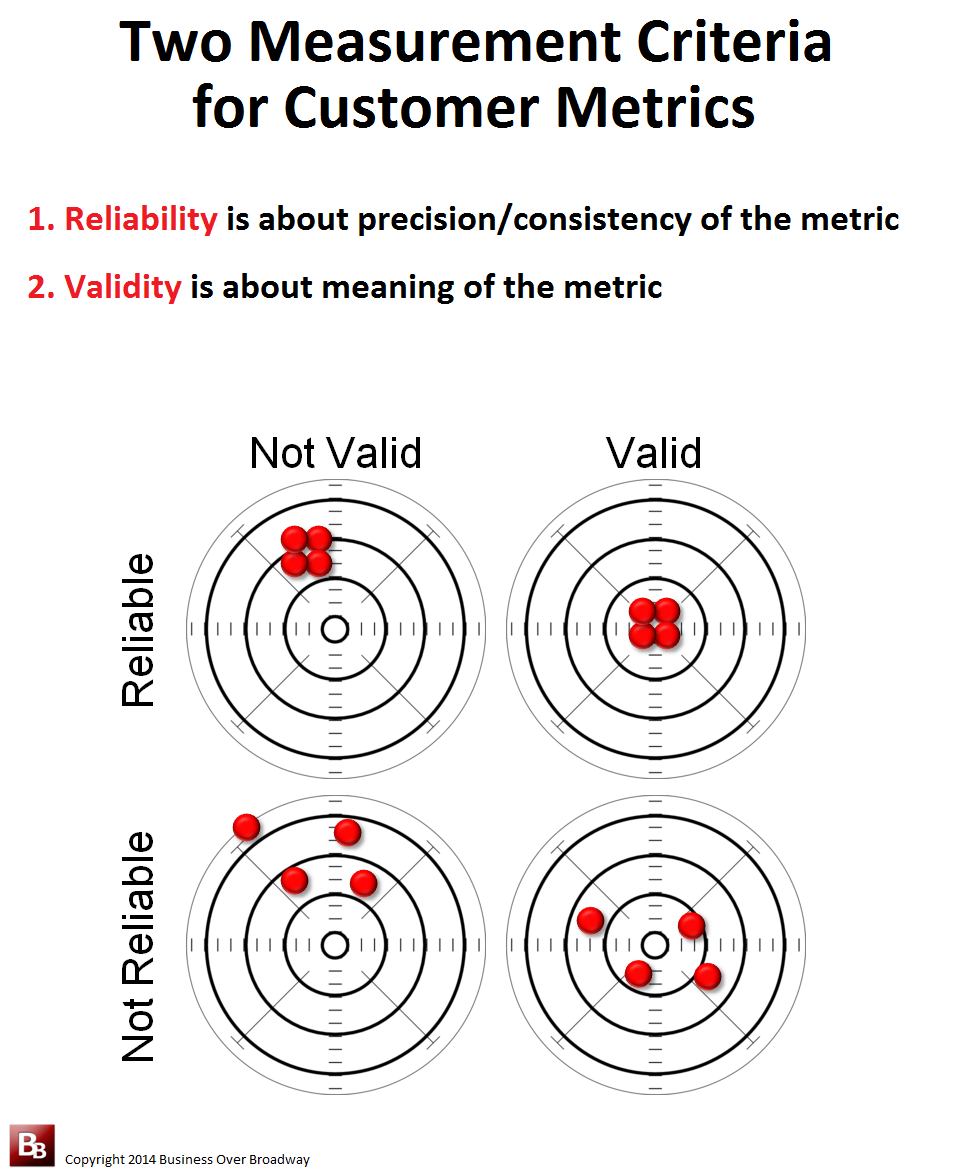
There are other pieces of validity evidence in addition to reliability that are used to determine the validity of a test score. Thus, we could say that the testing instrument is producing reliable weight values, but the values are not valid for their intended use because the scale is off by a few pounds. The results of each weighing may be consistent, but the scale itself may be off a few pounds. A test score could have high reliability and be valid for one purpose, but not for another purpose.Īn example often used for reliability and validity is that of weighing oneself on a scale. Reliability is a very important piece of validity evidence. Validity refers to the degree to which a test score can be interpreted and used for its intended purpose. Reliability refers to the degree to which scores from a particular test are consistent from one use of the test to the next. Technically, it is not the test itself but rather the resulting test score or rubric score that must have a high degree of reliability and validity. essays, performances, etc.) as being reliable and valid.
multiple-choice, true/false, etc.) or a constructed response test that requires rubric scoring (i.e.

It is common among instructors to refer to types of assessment, whether a selected response test (i.e. This variance in scores from group to group makes reliability and validity an important consideration when developing and administering assessments and evaluating student learning. This variance in student groups from semester to semester will affect how difficult or easy test items and tests will appear to be. Assessment data collected will be influenced by the type and number of students being tested. Since instructors assign grades based on assessment information gathered about their students, the information must have a high degree of validity in order to be of value. The purpose of testing is to obtain a score for an examinee that accurately reflects the examinee’s level of attainment of a skill or knowledge as measured by the test. Validity refers to whether the study or measuring test is measuring what is claims to measure.A basic knowledge of test score reliability and validity is important for making instructional and evaluation decisions about students. This can be split into internal and external reliability. Reliability refers to how consistent the results of a study are or the consistent results of a measuring test. What is difference between validity and reliability? Validity in data collection means that your findings truly represent the phenomenon you are claiming to measure. More specifically, validity applies to both the design and the methods of your research.


In general, VALIDITY is an indication of how sound your research is. Similarly, what is a validity in research? The ACT is valid (and reliable) because it measures what a student learned in high school. A test is valid if it measures what it's supposed to. Similarly, what is validity and reliability in research examples? Reliability implies consistency: if you take the ACT five times, you should get roughly the same results every time. The validity of a measurement tool (for example, a test in education) is the degree to which the tool measures what it claims to measure. Validity is the extent to which a concept, conclusion or measurement is well-founded and likely corresponds accurately to the real world. For example, if a weight measuring scale is wrong by 4kg (it deducts 4 kg of the actual weight), it can be specified as reliable, because the scale displays the same weight every time we measure a specific item. In simple terms, validity refers to how well an instrument as measures what it is intended to measure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
